H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Geometrical Optics, Exercise 4: EXERCISES
H C Verma Physics Solutions for Exercise - H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Geometrical Optics, Exercise 4: EXERCISES
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 18: Geometrical Optics, Exercise 4: EXERCISES with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. CONCEPTS OF PHYSICS [VOLUME 1] solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Geometrical Optics, Exercise 4: EXERCISES with Hints & Solutions
Two convex lenses, each of focal length , are placed at a separation of with their principal axes coinciding.
(a) Show that a light beam coming parallel to the principal axis diverges as it comes out of the lens system.
(b) Find the location of the virtual image formed by the lens system of an object placed far away.
(c) Find the focal length of the equivalent lens. (Note that the sign of the focal length is positive, although the lens system actually diverges a parallel beam incident on it).
A ball is kept at a height above the surface of a heavy transparent sphere made of a material of refractive index . The radius of the sphere is . At the ball is dropped to fall normally on the sphere. Find the speed of the image formed as a function of time for . Consider only the image by a single refraction.
A particle is moving at a constant speed from a large distance towards a concave mirror of radius along its principal axis. Find the speed of the image formed by the mirror as a function of the distance of the particle from the mirror.
A small block of mass and a concave mirror of radius fitted with a stand lies on a smooth horizontal table with a separation between them. The mirror together with its stand has a mass . The block is pushed at towards the mirror so that it starts moving towards the mirror at a constant speed and collides with it. The collision is perfectly elastic. Find the velocity of the image
(a) at a time ,
(b) at a time .
A gun of mass fires a bullet of mass with a horizontal speed . The gun is fitted with a concave mirror of focal length facing towards the receding bullet. Find the speed of separation of the bullet and the image just after the gun was fired.
A mass is dropped on a vertical spring of spring constant from a height as shown in figure.
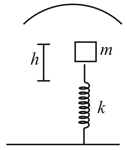
The mass sticks to the spring and executes simple harmonic oscillations after that. A concave mirror of focal length facing the mass is fixed with its principal axis coinciding with the line of motion of the mass, its pole being at a distance of from the free end of the spring. Find the length in which the image of the mass oscillates.
Two concave mirrors of equal radii of curvature are fixed on a stand facing opposite directions. The whole system has a mass and is kept on a frictionless horizontal table as shown in the figure. Two blocks and , each of mass , are placed on the two sides of the stand. At the separation between and the mirrors is and also the separation between and the mirrors is The block moves towards the mirror at a speed . All the collisions which take place are elastic. Taking the original position of the mirrors-stand system to be and -axis along . Find the position of the images of and at
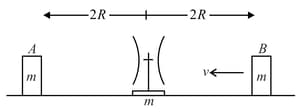
Consider the situation shown in figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration of and the focal length of the mirror is . All the surfaces are smooth and the pulley is light. The mass-pulley system is released from rest (with respect to the elevator) at when the distance of from the mirror is . Find the distance between the image of the block and the mirror at . Take .